Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2014; 5(4): 444-470
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.444
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.444
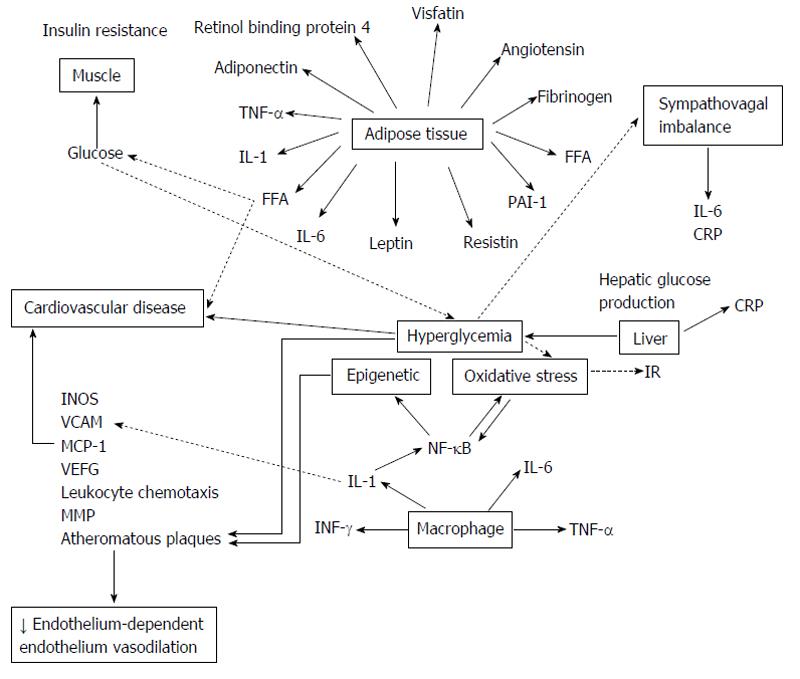
Figure 5 Pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease in diabetes.
The mechanisms implicated in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease in diabetes comprehend epigenetic changes and intracellular metabolic changes that result in oxidative stress, low-grade inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction. CRP: C-reactive protein; FFA: Free fatty acids; INOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL-1: Interleukin 1; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant molecule 1; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-β; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule; VEFG: Vascular endothelial growth factor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; INF-γ: Interferon-γ; IR: Insulin resistance.
- Citation: Martín-Timón I, Sevillano-Collantes C, Segura-Galindo A, Cañizo-Gómez FJD. Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Have all risk factors the same strength? World J Diabetes 2014; 5(4): 444-470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v5/i4/444.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.444