Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2013; 4(4): 101-113
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.101
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.101
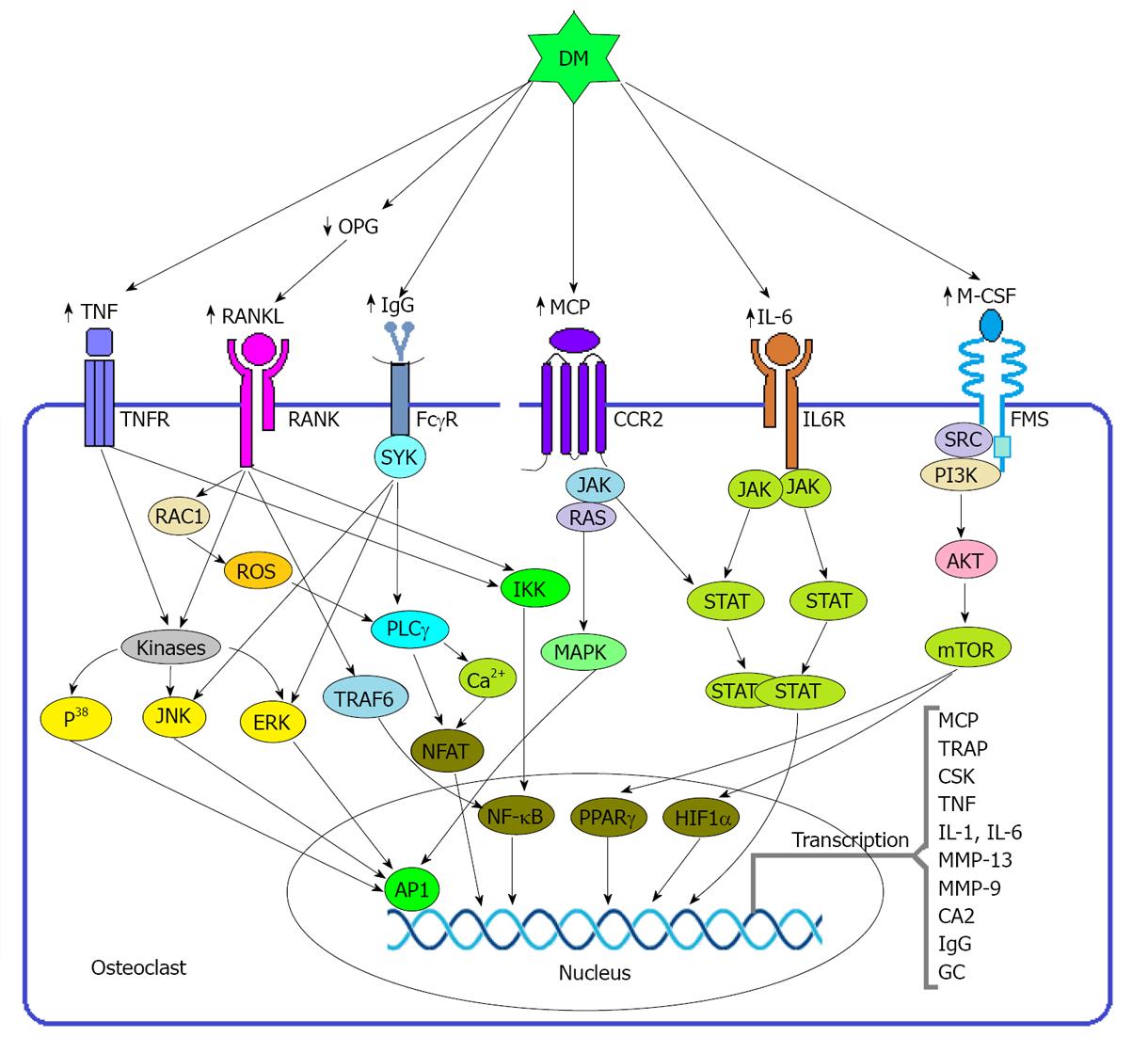
Figure 3 Diabetes mellitus induced regulation of osteoclast.
During normal physiology several osteoblastogenic modulators including RANKL, M-CSF, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP), and immunoglobulin G (IgG) binds with their receptors expressed on osteoclast and activates different signal transduction pathway to transcribe the particular gene. Binding of RANKL with RANK triggers several possible pathways to induce the corresponding element. It may induce transcription factor NF-κB through TRAF or IkB kinase (IKK) mediated pathway as well as induces nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) through reactive oxygen species (ROS)- phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ) mediated pathway. RANK also may induce AP-1 through triggering the kinase enzymes. Macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) activates transcription factors peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and hypoxia inducible factor 1 α (HIF1α) through PI3K-AKT mediated pathway. MCP activates AP-1 signaling through RAS-MAPK mediated pathway which requires the assistance of JAK. IgG also signals through the Fc receptor γ chain (FcγR) to activate NFAT via the induction of PLCγ as well as activates AP-1 through the kinase enzyme systems and both of the pathways require the activation of SYK. \During the state of DM, it induces the upregulation of osteoclastogenic factors stated above and thereby induce the differentiation and activity of osteoclast. In addition to the above factors, DM also induces the synthesis of some proinflammatory cytokines which also favor the bone resorption by osteoclast. interleukin 6 (IL-6) exerts its effect through JAK-STAT mediated pathway although MCP activated JAK may contribute to the activation of STAT to some extent. TNF also activates NF-κB and AP-1 through IKK and Kinase system respectively. CCR2: CC chemokine receptor 2; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; OPG: Osteoprotegerin; ERK: Extracellular signal regulated kinase; JNK: JUN N terminal kinase; TRAP: Tartrate resistant acid phosphatase; CSK: Cathepsin K; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; CA2: Carbonic anhydrase 2; GC: Glucocorticoid.
- Citation: Roy B. Biomolecular basis of the role of diabetes mellitus in osteoporosis and bone fractures. World J Diabetes 2013; 4(4): 101-113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v4/i4/101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v4.i4.101