Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2025; 16(8): 106833
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.106833
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.106833
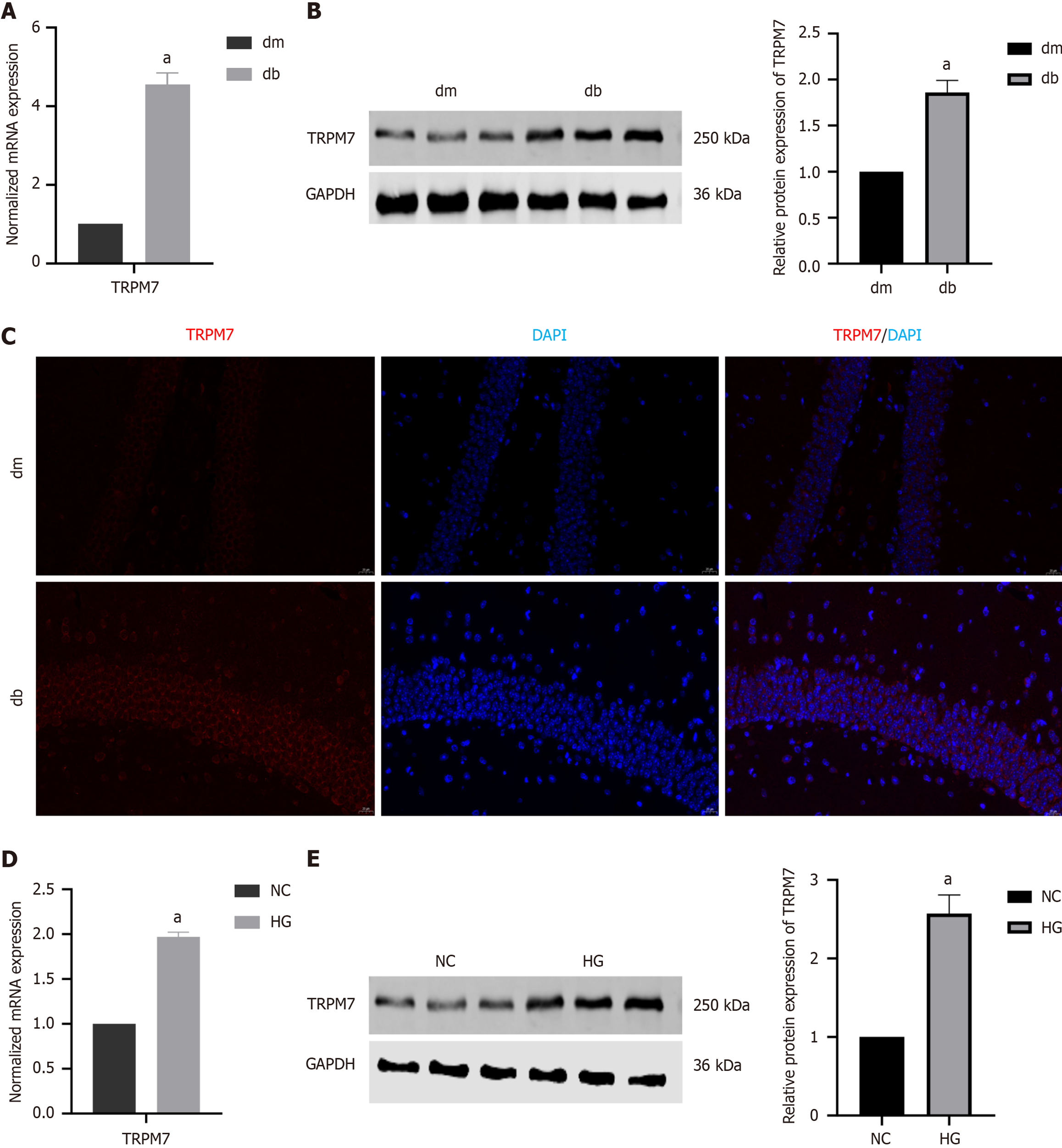
Figure 3 The level of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 was increased in diabetic cognitive dysfunction mice and hippocampal neuronal cells dealed with high-concentration glucose.
A: The normalized mRNA expression of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) in the hippocampal tissue; B: The relative protein expression of TRPM7 in the hippocampal tissue; C: Immunofluorescent staining of TRPM7 in the hippocampal tissue; D: The normalized mRNA expression of TRPM7 in high-concentration glucose-treated hippocampal neuronal cells; E: The relative protein expression of TRPM7 in high-concentration glucose-treated hippocampal neuronal cells. aP < 0.05, compared with dm group or normal control group. Data presented as mean ± SEM. dm: Control group; db: Diabetes group; NC: Normal control; HG: Hypertonic group (100 mmol/L glucose); DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; TRPM7: Transient receptor potential melastatin 7.
- Citation: Li J, Gao M, Wang JX, Li HY, Wang P, Yuan F, Liu AJ, Zhang SY. Troxerutin improves diabetic cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting mitochondrial fission mediated by transient receptor potential melastatin 7/calcineurin/dynamin-related protein 1ser637. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(8): 106833
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i8/106833.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.106833