Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2025; 16(7): 108789
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.108789
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.108789
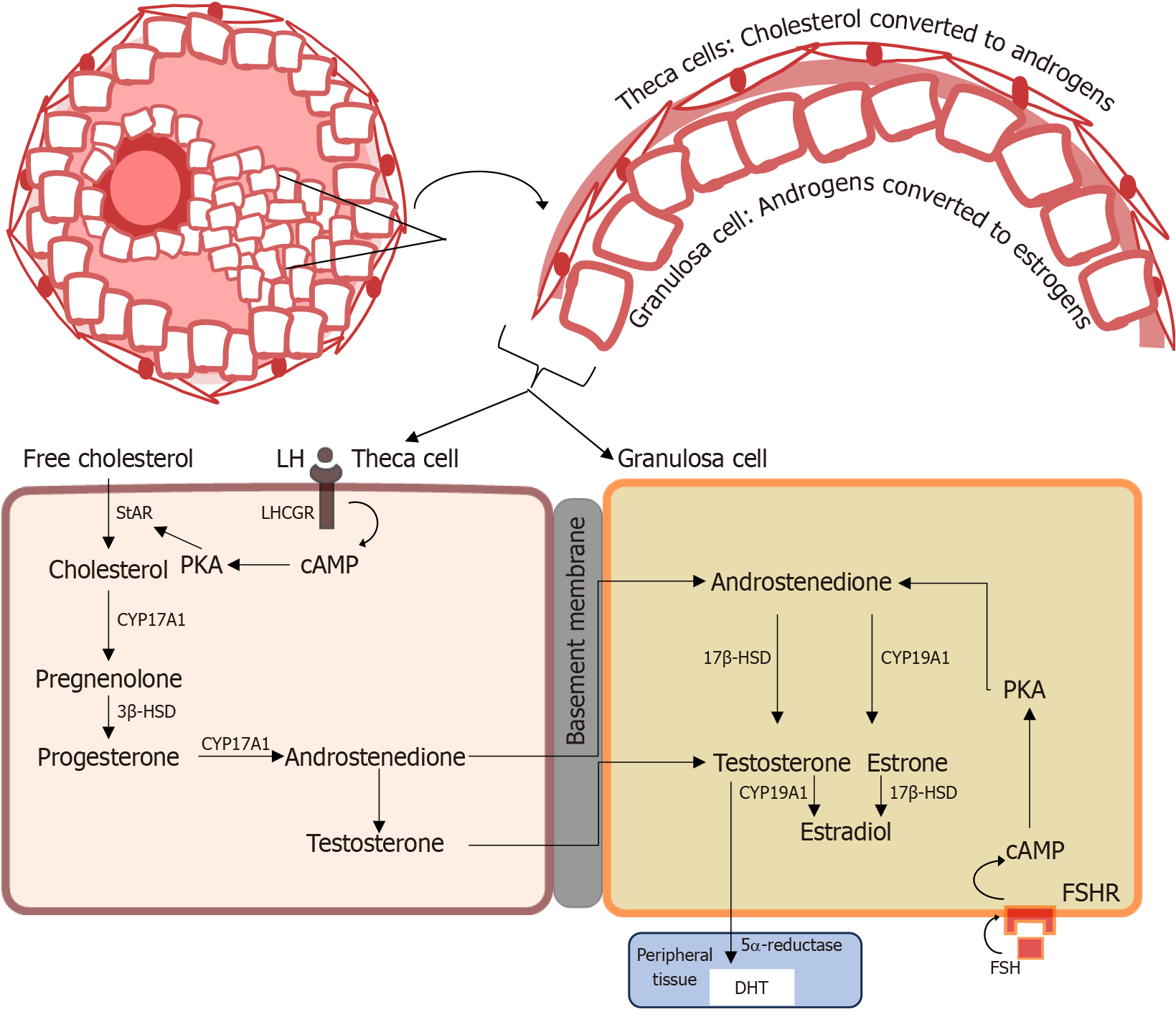
Figure 2 Steroid biosynthesis in the ovary shows the two-cell, two-gonadotropin model, where androgens synthesized in the theca cells are aromatized to estrogens in the granulosa cells, under normal physiological conditions.
In the initial synthesis of androgen, under the control of luteinizing hormone, the side chain of cholesterol is cleaved by the P450 side chain cleavage enzyme, cytochrome P450 17A1, to pregnenolone, a precursor to all steroid hormones. Testosterone is a precursor converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol in target tissue by 5α-reductase and the aromatase enzyme, respectively. LH: Luteinizing hormone; LHCGR: Luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA: Protein kinase A; StAR: Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; CYP17A1: Cytochrome P450 17A1; 3β-HSD: 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; 17β-HSD: 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; CYP19A1: Cytochrome P450 19A1; FSHR: Follicle-stimulating hormone receptor; FSH: Follicle-stimulating hormone; DHT: 5α-dihydrotestosterone.
- Citation: Rambaran N, Islam MS. Decoding androgen excess in polycystic ovary syndrome: Roles of insulin resistance and other key intraovarian and systemic factors. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(7): 108789
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i7/108789.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.108789