Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2025; 16(7): 104512
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.104512
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.104512
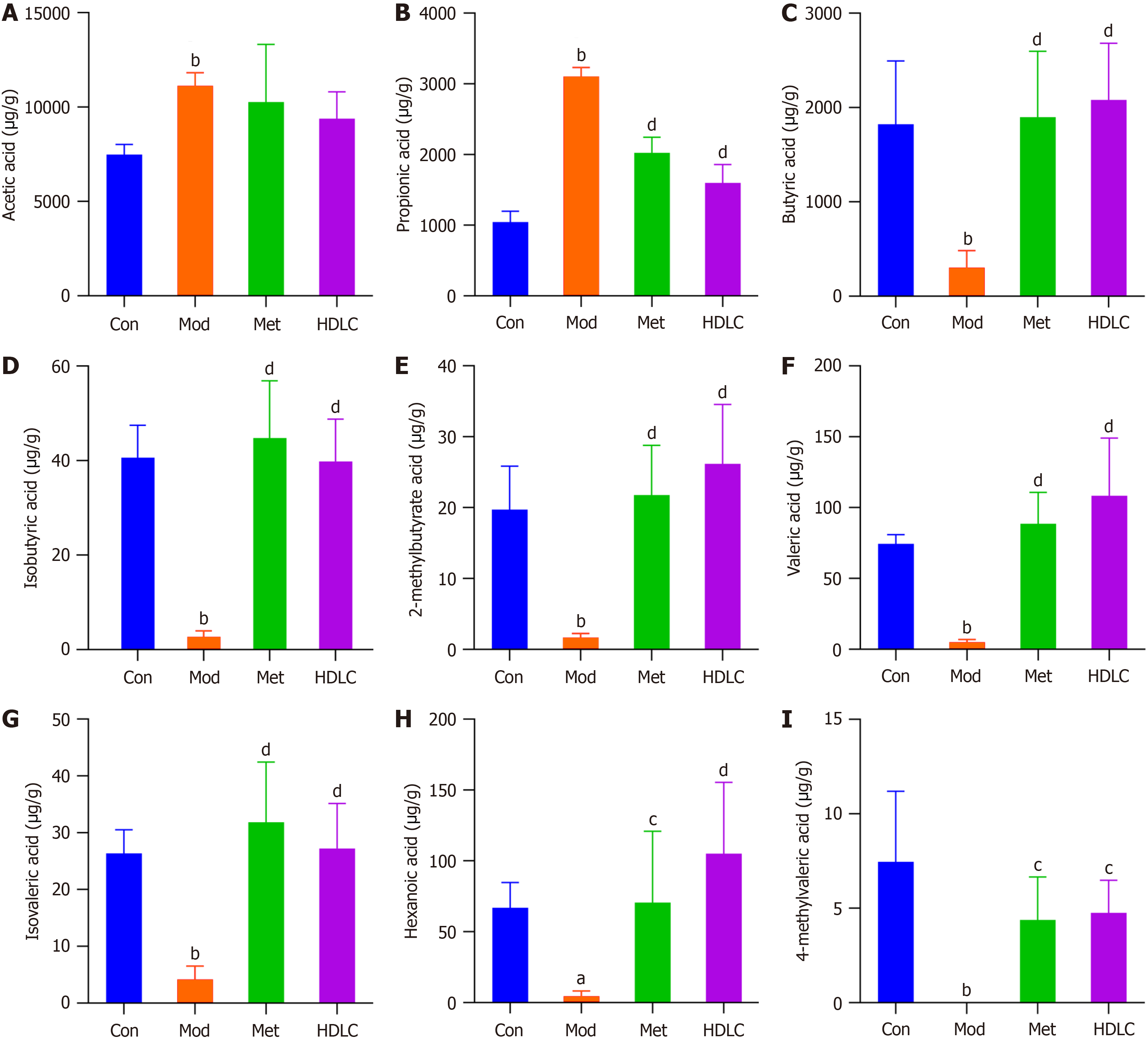
Figure 5 Effects of Dimocarpus longan Lour leaf components on short-chain fatty acids in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats.
A: Acetic acid; B: Propionic acid; C: Butyric acid; D: Isobutyric acid; E: 2-Methylbutyrate acid; F: Valeric acid; G: Isovaleric acid; H: Hexanoic acid; I: 4-Methylvaleric acid. Results were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs the control (Con) group; bP < 0.01 vs the Con group; cP < 0.05 vs the model (Mod) group; dP < 0.01 vs the Mod group. Con: Control group; Mod: The model group; Met: The metformin group; HDLC: The high-dose group.
- Citation: Zheng PX, Lu CL, Liang YL, Ma YM, Peng JW, Xie JJ, Wei JL, Chen SS, Ma ZD, Zhu H, Liang J. Examining gut microbiota and metabolites to clarify mechanisms of Dimocarpus longan Lour leaf components against type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(7): 104512
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i7/104512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.104512