Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 103370
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.103370
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.103370
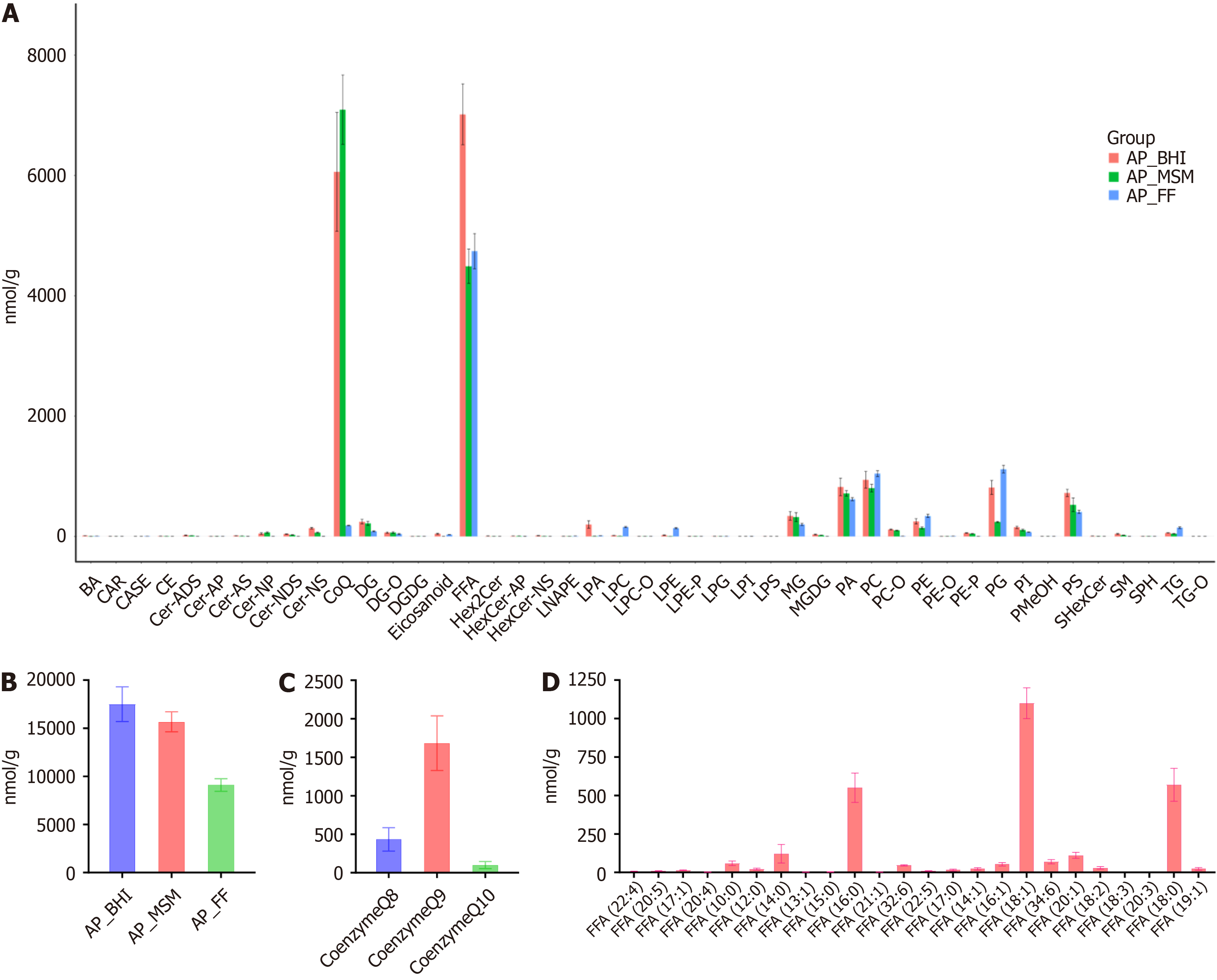
Figure 4 Lipid analysis of Acetobacter pasteurianus.
A: Changes in the content of lipid subclasses; B: Total lipid content variation; C: Comparison of the contents of three types of coenzyme Q; D: Comparison of the contents of 24 types of free fatty acids. Metabolomics testing was performed on Acetobacter pasteurianus from brain heart infusion (BHI) culture, chromium-rich zinc-rich culture, and mineral salt medium culture. AP: Alkylphospholipid; BA: Bile acid; CAR: Cardiolipin; CASE: Sitosterol acetate; CE: Cholesteryl ester; Cer-ADS: Ceramide-1-acetate; Cer-AP: Ceramide-1-phosphate; Cer-AS: Ceramide-1-sulfate; Cer-NP: Ceramide-N-phosphocholine; Cer-NDS: Ceramide-N-phosphoethanolamine; Cer-NS: Ceramide-N-sulfate; CoQ: Coenzyme Q; DG: Diacylglycerol; DGDG: Digalactosyldiacyl glycerol; DG-O: Diacylglycerol-plasmalogen; FFA: Free fatty acid; LPA: Lysophosphatidic acid; LPC: Lysophosphatidyl choline; LPC-O: Lysophosphatidyl choline-plasmalogen; LPE: Lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine; LPE-P: Lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine-plasmalogen; LPG: Lysophosphatidyl glycerol; LPI: Lysophosphatidyl inositol; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MG: Monoacylglycerol; MGDG: Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol; MSM: Mineral salt medium; PA: Phosphatidic acid; PC: Phosphatidylcholine; PE: Phosphatidylethanolamine; PE-O: Plasmalogen phosphatidylethanolamine; PE-P: Phosphatidylethanolamine-plasmalogen; PG: Phosphatidylglycerol; PI: Phosphatidylinositol; PMeOH: Phosphatidyl methanol; PS: Phosphatidylserine; SM: Sphingomyelin; SPH: Sphingosine; TG: Triacylglycerol; TG-O: Triacylglycerol-plasmalogen.
- Citation: Xu WY, Zhou WT, Luo JZ, Jiang YY, Zhang K, Zhang SY, Liu PS, Wei HY, Huang YQ. Lipid metabolism of Acetobacter pasteurianus and its main components with hypoglycemic effects. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 103370
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/103370.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.103370