Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 102727
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.102727
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.102727
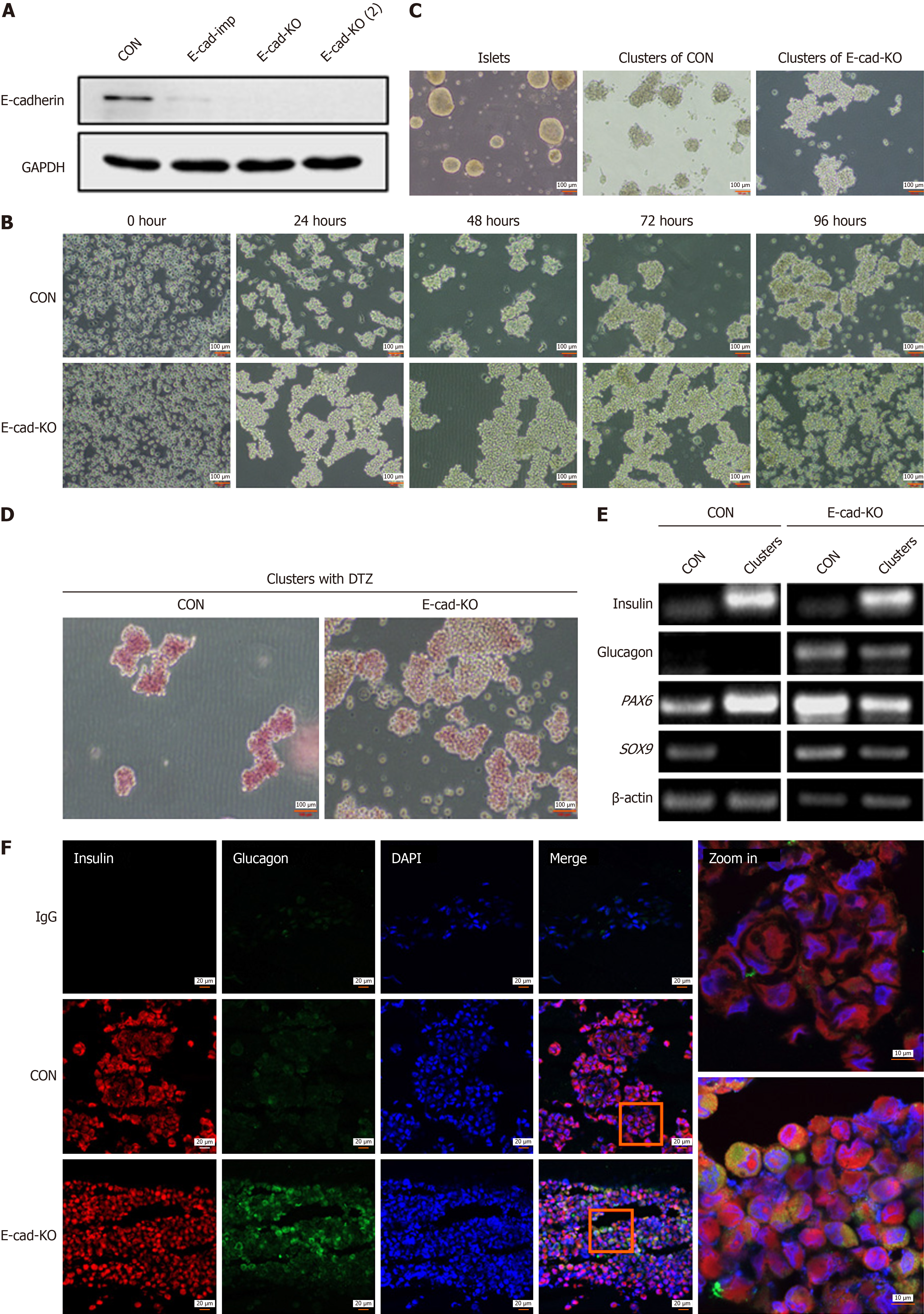
Figure 1 E-cadherin contributes to aggregation of human pancreatic cancer cell line-1 into islet-like clusters induced by trypsin.
A: Expression of E-cadherin protein was detected by western blotting, reflecting knockout (KO) efficiency of E-cadherin 1 gene (CDH1), E-cad-imp group: Stable transgenic cells with CDH1 gene KO by clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)- -associated 9 (Cas9) system impure, E-cad-KO and E-cad-KO (2): Monoclonal cells screening from stable KO cells; B: Representative images of KO cells at five time points after digestion with trypsin before and after CDH1 KO, magnification 10 ×; C: Morphology of islet-like cell clusters differentiated in vitro was compared with that of natural islets; D: Representative image of diphenylterazine (DTZ) staining of cell clusters formed at 96 hours before and after CDH1 KO, magnification 10 ×; E: Polymerase chain reaction detection reflected the changes in expression of the transcripts for mature islet-related genes insulin, glucagon, paired box 6 (PAX6), SRY-box transcription factor 9 (SOX9) before and after CDH1 KO; F: Representative immunofluorescence images of insulin, glucagon, and 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) signal in differentiated cell clusters before and after CDH1 KO, magnification 20 ×, increased to 63 ×. CON: Control; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Gao L, Lai JS, Chen H, Qian LX, Hong WJ, Li LC. Mechanism of trypsin-mediated differentiation of pancreatic progenitor cells into functional islet-like clusters. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 102727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/102727.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.102727