Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
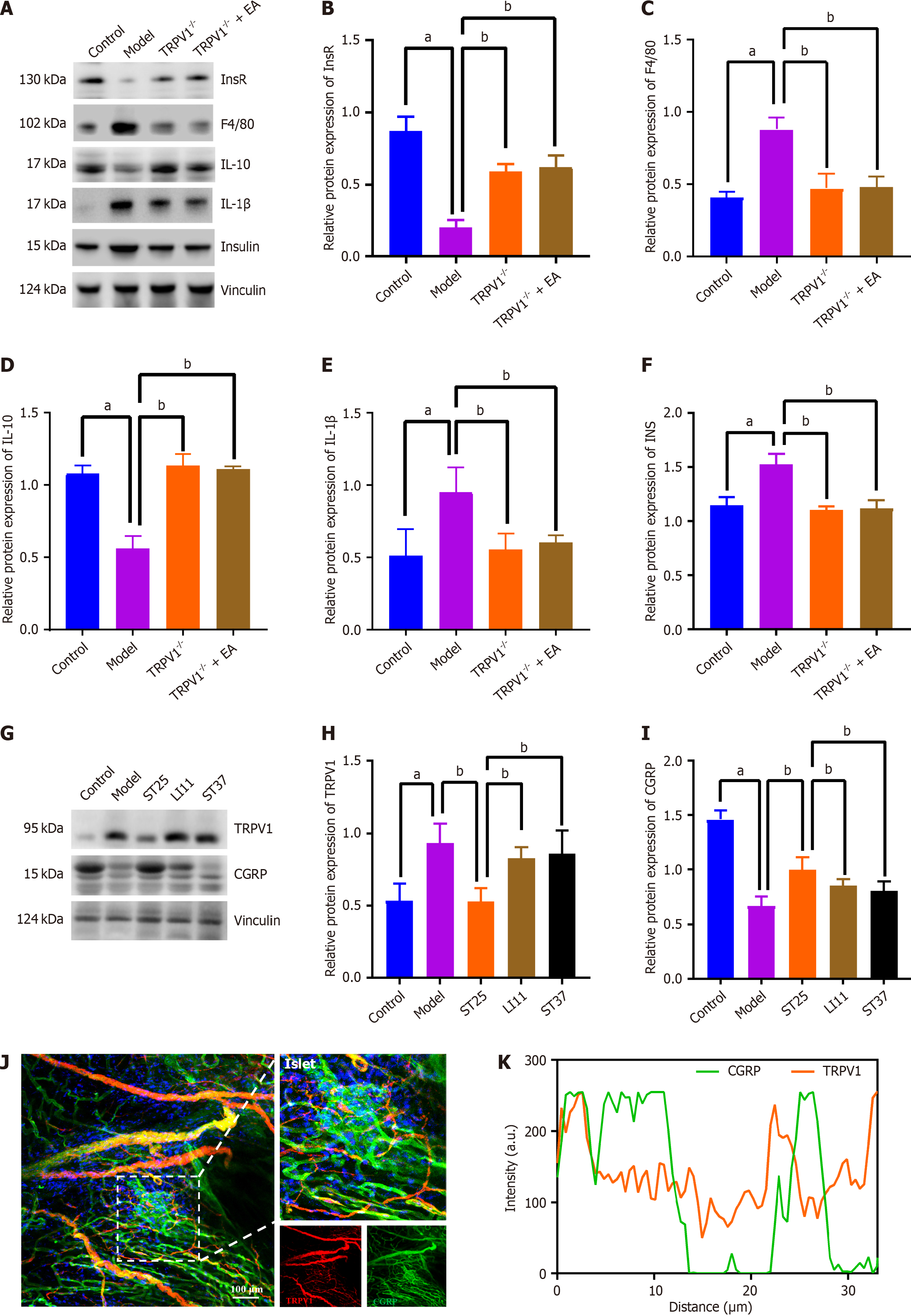
Figure 6 TRPV1 knockout preserves immunometabolic homeostasis in peripancreatic adipose tissue and pancreas.
A-F: Impact of electroacupuncture (EA) on the levels of insulin receptor, EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 1 (F4/80), interleukin (IL)-10, IL-1β, and insulin in peripancreatic adipose tissue following TRPV1 knockout; G-I: Influence of EA on the expression levels of TRPV1 and calcitonin gene-related peptide-receptor component protein (CGRP) in the pancreas. Vinculin served as loading controls; J: Representative immunofluorescence images of co-expression of TRPV1 and CGRP in the islets of the ST25 group (200 × magnification). Nuclei were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue), TRPV1 is represented by red immunofluorescence, and CGRP by green immunofluorescence; K: Correlation between TRPV1 and CGRP expression as revealed by quantitative analysis of the co-localization of TRPV1 and CGRP immunofluorescence. aP < 0.05 compared to the normal control group; bP < 0.05 compared to the model or another treatment group. IL: Interleukin; EA: Electroacupuncture
- Citation: Liu Y, Yu Z, Wang X, Yuan MQ, Lu MJ, Gong MR, Li Q, Xia YB, Yang GH, Xu B, Litscher G, Xu TC. Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 101354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/101354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354