Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354
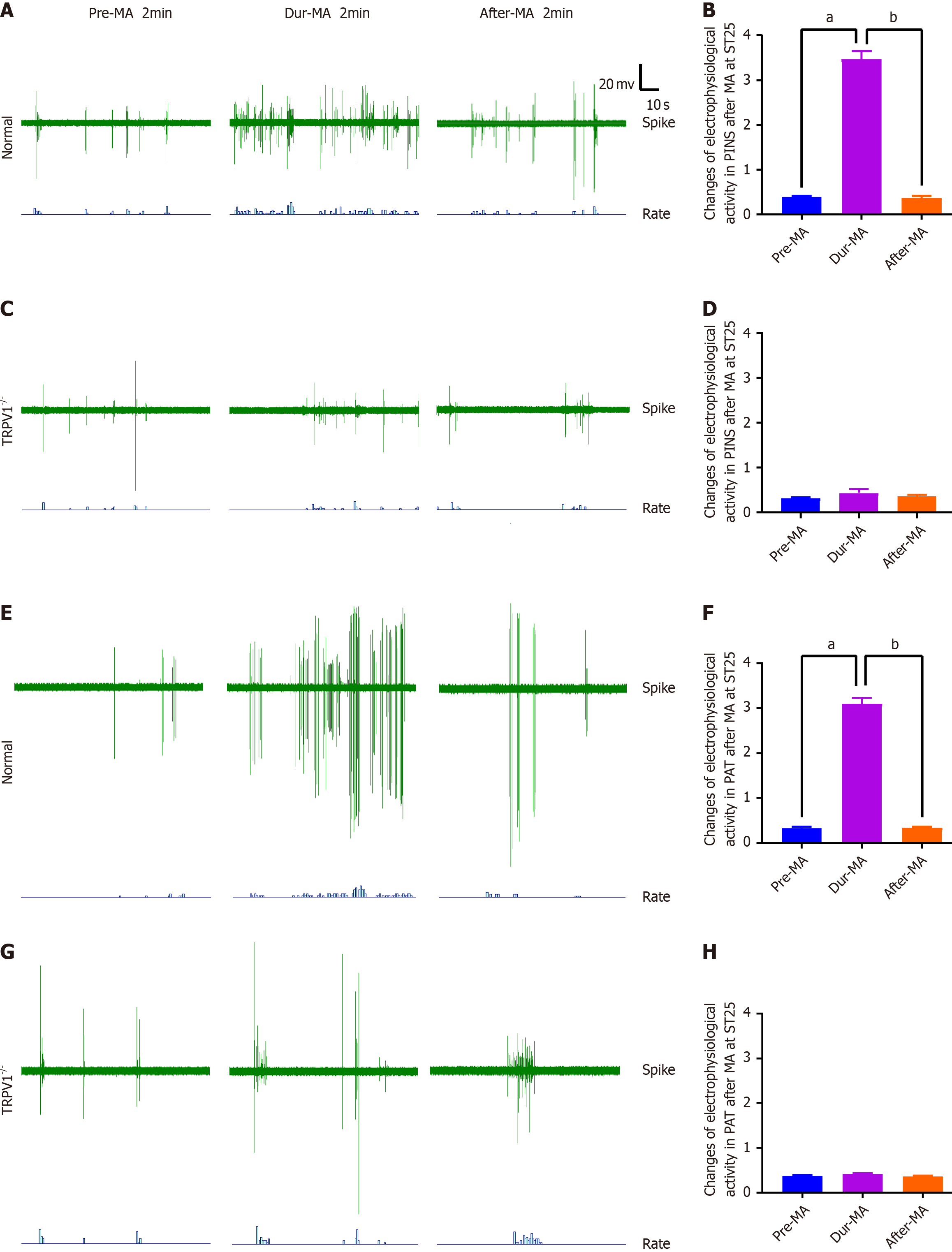
Figure 3 TRPV1-mediated acupuncture modulates the discharge patterns of the pancreatic intrinsic nervous system.
A and B: The impact of manual acupuncture (MA) at Tianshu (ST25) acupoint on pancreatic intrinsic nervous system (PINS) activity and the corresponding discharge frequency in wild-type (WT) mice; C and D: The influence of MA at ST25 on PINS activity and discharge frequency in TRPV1 knockout (TRPV1-/-) mice; E and F: The effect of MA at ST25 on peripancreatic adipose tissue (PAT) activity and associated discharge frequency in WT mice; G and H: The alteration in PAT activity and discharge frequency following MA at Tianshu (ST25) acupoint in TRPV1-/- mice (n = 7). aP < 0.01 compared to the dur-MA group; bP < 0.01 compared to the pre-MA group and MA, manual acupuncture. TRPV1: Transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily member 1; MA: Manual acupuncture.
- Citation: Liu Y, Yu Z, Wang X, Yuan MQ, Lu MJ, Gong MR, Li Q, Xia YB, Yang GH, Xu B, Litscher G, Xu TC. Neurophysiological mechanisms of electroacupuncture in regulating pancreatic function and adipose tissue expansion. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 101354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/101354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101354