Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2024; 15(2): 260-274
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.260
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.260
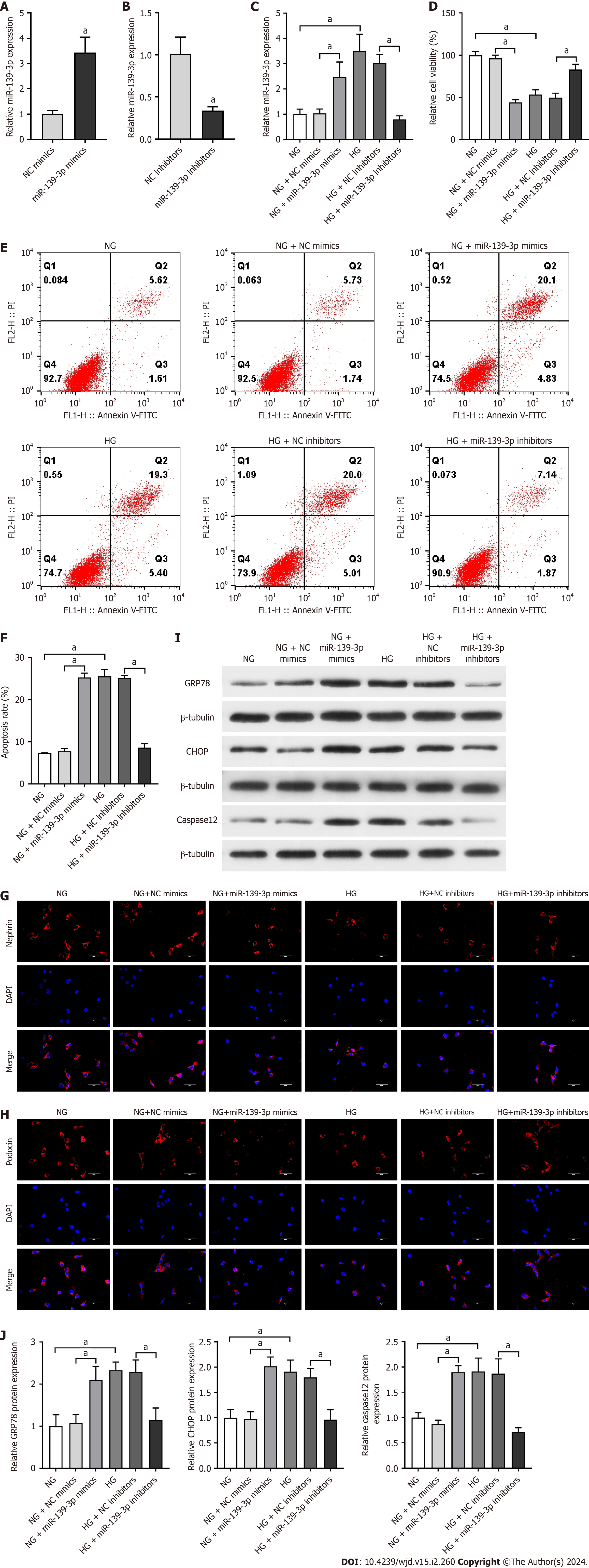
Figure 4 Inhibition of miR-139-3p attenuated podocyte apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in high glucose-cultured podocytes.
The overexpression of miR-139-3p aggravated podocyte apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in normal glucose-cultured podocytes. A: The transfection efficiency of miR-139-3p mimics was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); B: The transfection efficiency of miR-139-3p inhibitors was detected by qRT-PCR; C: The expression of miR-139-3p was measured by qRT-PCR. U6 served as the loading control; D: Quantitative analysis of the relative cell viability; E: Podocyte apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry; F: Quantitative analysis of cell apoptotic rate; G and H: The expressions of nephrin and podocin in podocytes were analyzed by immunofluorescence. Scale bar = 50 μm; I: The protein expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related factors (glucose-regulated protein 78, C/EBP homologous protein, and caspase-12) was analyzed by western blotting. β-Tubulin served as an internal control; J: Quantitative analysis of glucose-regulated protein 78, C/EBP homologous protein and caspase-12. The data were presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. lncRNA: Long noncoding RNA; HG: High glucose; NG: Normal glucose; Pdia3: Protein-disulfide isomerase-associated 3; GRP78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein.
- Citation: He YX, Wang T, Li WX, Chen YX. Long noncoding RNA protein-disulfide isomerase-associated 3 regulated high glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy through targeting miR-139-3p. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(2): 260-274
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i2/260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.260