Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2023; 14(11): 1603-1620
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1603
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1603
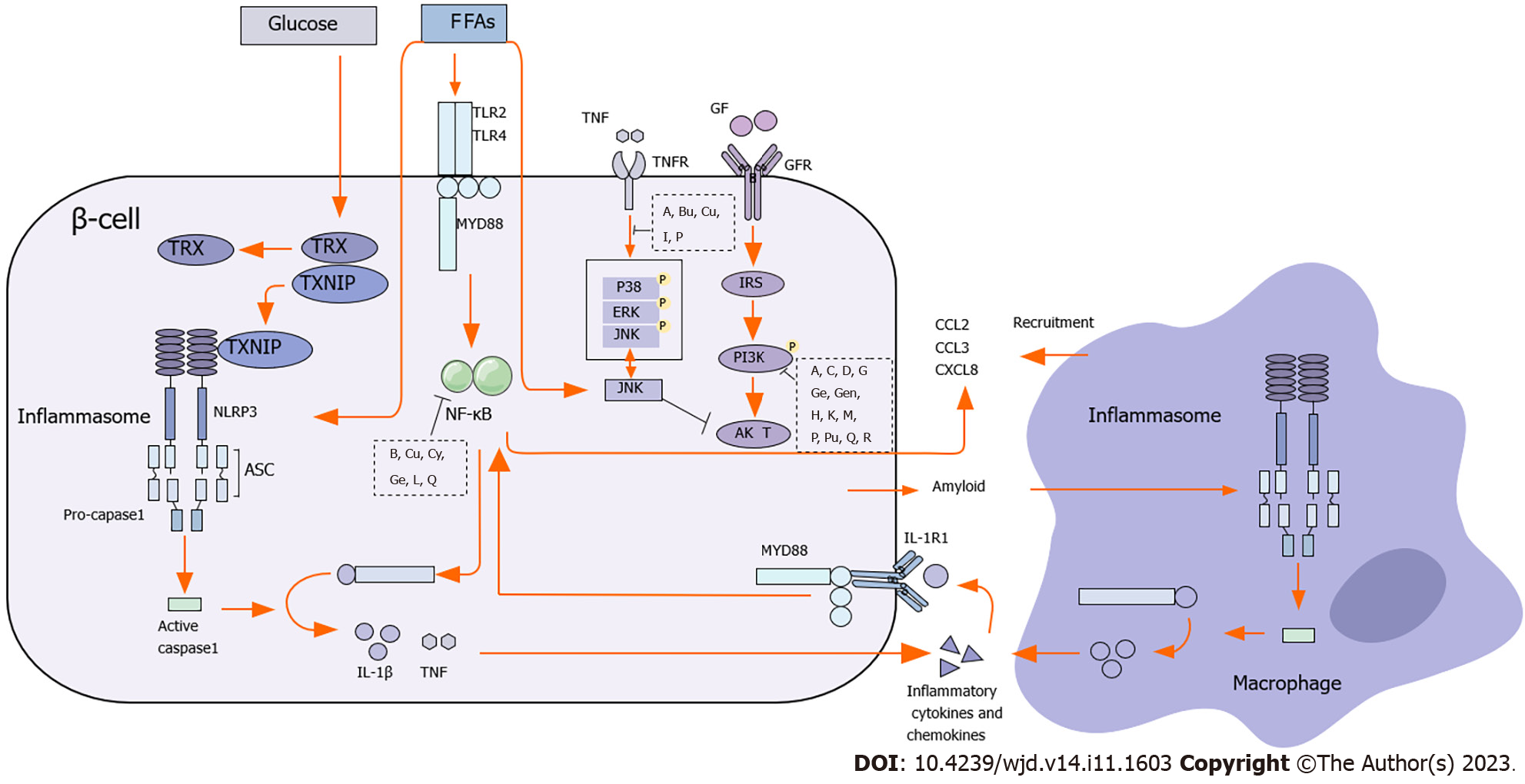
Figure 2 The mechanism of natural products suppresses insulin resistance.
The letters inside the black squares refer to natural products. A: Alpha-mangostin; B: Berberine; Bu: Butein; C: Caffeic acid; Cu: Curcumin; Cy: Cyanidin-3-glucoside; D: Dioscorea batatas extract; G: Gallic acid; Ge: Genistein; Gen: Geniposide; H: Hesperidin; I: Icarrin; K: Kaempferol; L: Leteolin; M: Mulberry anthocyanin extract; P: Paeoniflorin; Pu: Puerarin; Q: Quercetin; R: Resveratrol; CHOP: CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; ER stress: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; FFA: Free fatty acids; FOXO: Forkhead box class O; GFR: Growth factor receptor; GR: Growth factor; IKK: Inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappa B kinase; IL-1β: Interleukin 1β; IL-1: Interleukin 1; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; IRAK: Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; NO: Nitric oxide; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ROS/RNS: Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor.
- Citation: Wang T, Wang YY, Shi MY, Liu L. Mechanisms of action of natural products on type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(11): 1603-1620
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i11/1603.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1603