Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2023; 14(1): 26-34
Published online Jan 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i1.26
Published online Jan 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i1.26
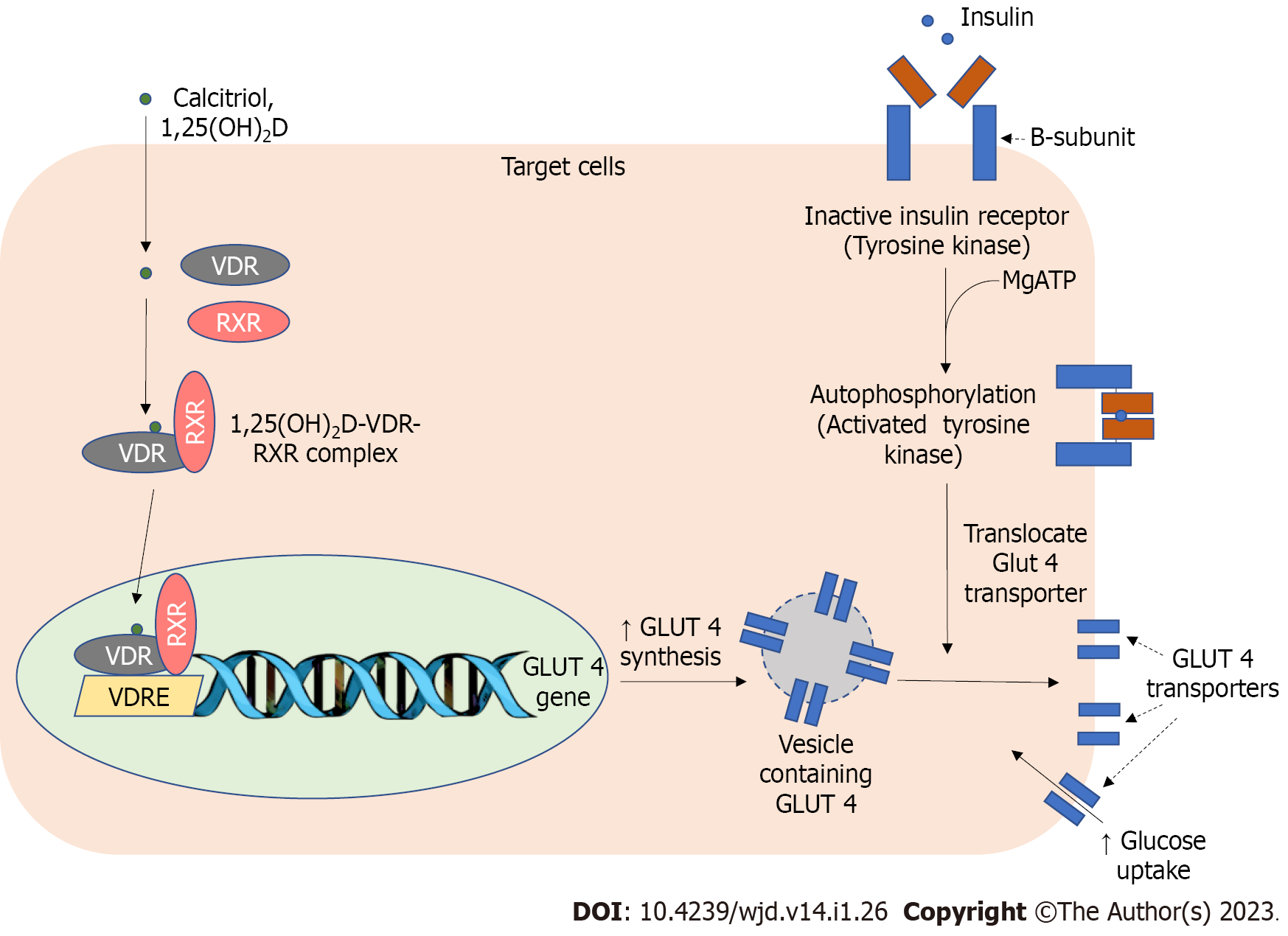
Figure 2 Interrelation of vitamin D and magnesium in the action of insulin at target organs.
Magnesium adenosine triphosphate plays a role in the autophosphorylation process of B-subunits of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase, a crucial step in initiating an intracellular signaling pathway. The calcitriol-vitamin D receptors-retinoid X receptor-vitamin D response element complex also modulates the synthesis of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4), a predominant glucose transporter present in muscle cells and adipocytes. Upon stimulation by insulin, the activated tyrosine kinase receptor will stimulate the fusion of vesicles containing GLUT4 to the cellular membrane. This process increases cellular glucose uptake. GLUT/4: Glucose transporter type 4; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; VDRE: Vitamin D response element; MgATP: Magnesium adenosine triphosphate; Ca2+: Calcium; VDR: Vitamin D receptors; 1,25(OH)2 D: 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D.
- Citation: Wan Nik WNFH, Zulkeflee HA, Ab Rahim SN, Tuan Ismail TS. Association of vitamin D and magnesium with insulin sensitivity and their influence on glycemic control. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(1): 26-34
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i1/26.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i1.26