Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2022; 13(11): 926-939
Published online Nov 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.926
Published online Nov 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.926
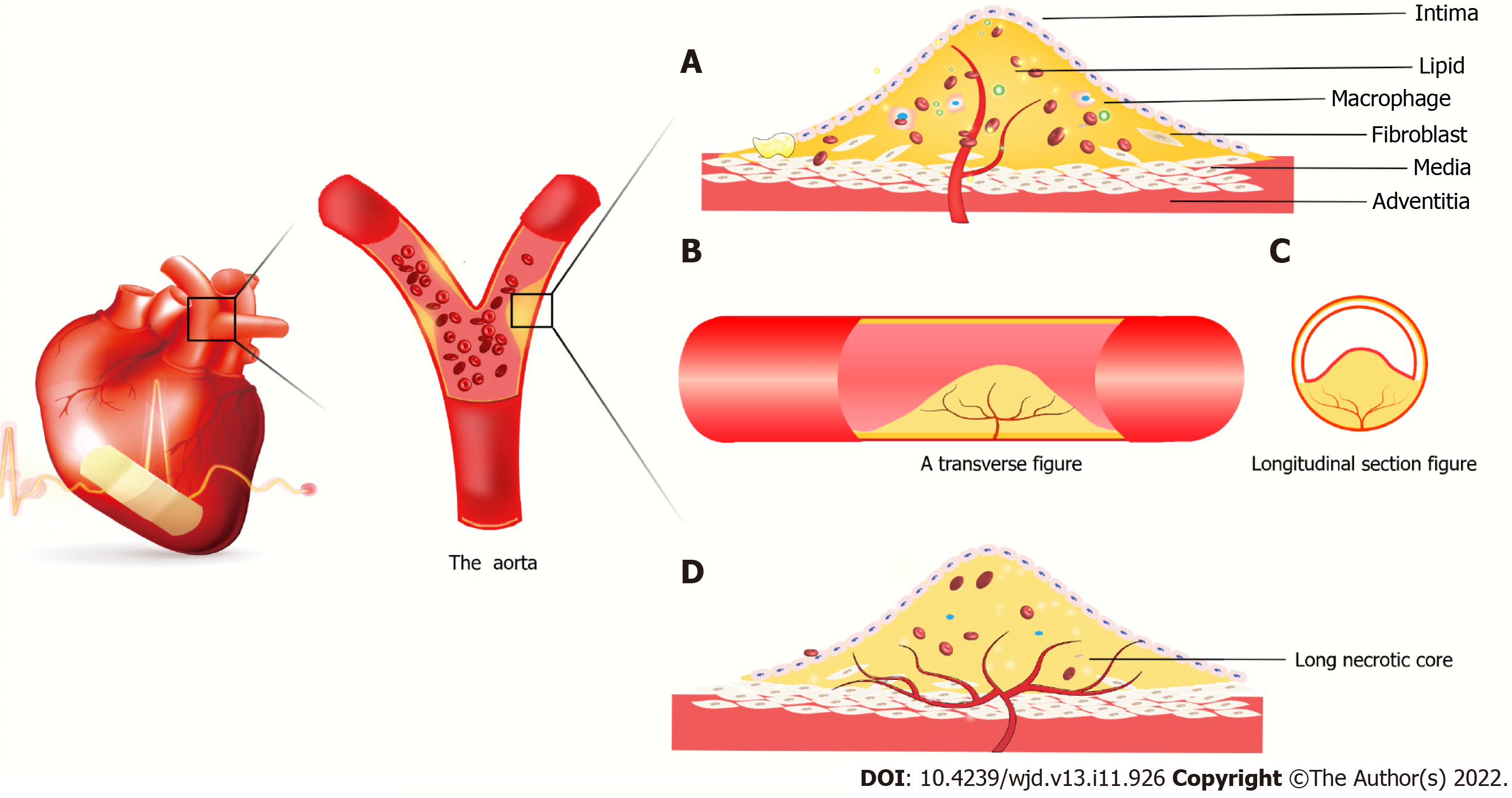
Figure 3 Atherosclerotic plaque forms in coronary vessels.
A: New blood vessels from the outer membrane to the media and intima, macrophages and smooth muscle cells gobble up from the film in lipid foam cell formation. The red blood cells, cytokines, etc extend the blood vessels into the plaque. It is because the spin-off of new blood vessels leads to unstable plaques, plaque hemorrhage and rupture resulting in acute coronary syndrome; B: Axial slice of intravascular plaque and neovascularization grows axially in the plaque; C: Transverse view of intravascular plaque; D: It is believed that neovascularization grows in the axial direction in plaques. Due to insufficient growth of neovascularization, long necrotic plaques are ruptured due to ischemia and hypoxia in the plaque, resulting in acute coronary syndrome.
- Citation: Cai Y, Zang GY, Huang Y, Sun Z, Zhang LL, Qian YJ, Yuan W, Wang ZQ. Advances in neovascularization after diabetic ischemia. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(11): 926-939
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i11/926.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.926