Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2021; 12(1): 19-46
Published online Jan 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i1.19
Published online Jan 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i1.19
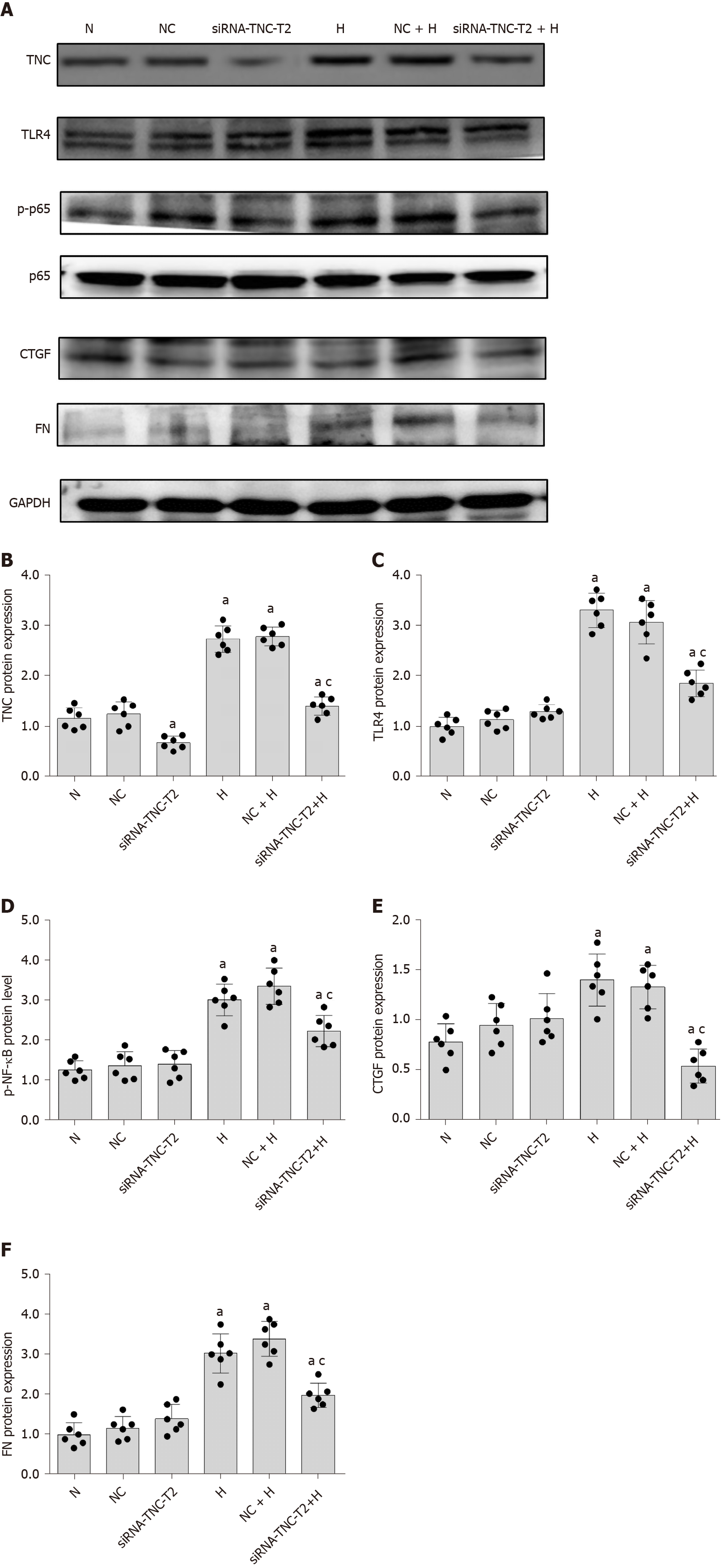
Figure 5 Silencing of tenascin-C protein expression inhibits the expression of Toll-like receptor-4 and fibrosis factors (connective tissue growth factor and fibronectin), as well as the phosphorylation of p65.
A: Protein bands; B-F: Protein expression of tenascin-C (TNC), Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4), phosphorylated nuclear factor-κB p65 (Ser536) (p-NF-κB p65), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), and fibronectin (FN). Rat mesangial cells (RMCs) were transfected with siRNA-TNC-T2 for 6 h, and the media were then replaced with normal-glucose (NG, 5.5 mmol/L glucose) or high-glucose (HG, 30 mmol/L glucose) medium for 24 h (N, 5.5 mmol/L glucose). RMCs were transfected with siRNA-TNC-T2 and siRNA-NC for 6 h, and the media were then replaced with normal-glucose (NG, 5.5 mmol/L glucose) or high-glucose (HG, 30 mmol/L glucose) medium for 24 h. aP < 0.05 compared with RMCs cultured with normal glucose concentrations; cP < 0.05 compared with RMCs cultured with high glucose concentrations. TNC, TLR4, p-NF-κB p65, NF-κB p65, CTGF, and FN levels were all detected using Western blot. The results are presented as the mean ± SD of six independent experiments after normalization to GAPDH levels. TNC: Tenascin-C; TLR4: Toll-like receptor-4; p-p65: Phosphorylated nuclear factor-κB p65 (Ser536); p65: Nuclear factor-κB p65; CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; FN: Fibronectin; N: Normal control; NC: Negative control; H: High glucose.
- Citation: Zhou Y, Ma XY, Han JY, Yang M, Lv C, Shao Y, Wang YL, Kang JY, Wang QY. Metformin regulates inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease through TNC/TLR4/NF-κB/miR-155-5p inflammatory loop. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(1): 19-46
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i1/19.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i1.19