Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2022; 13(11): 949-961
Published online Nov 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.949
Published online Nov 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.949
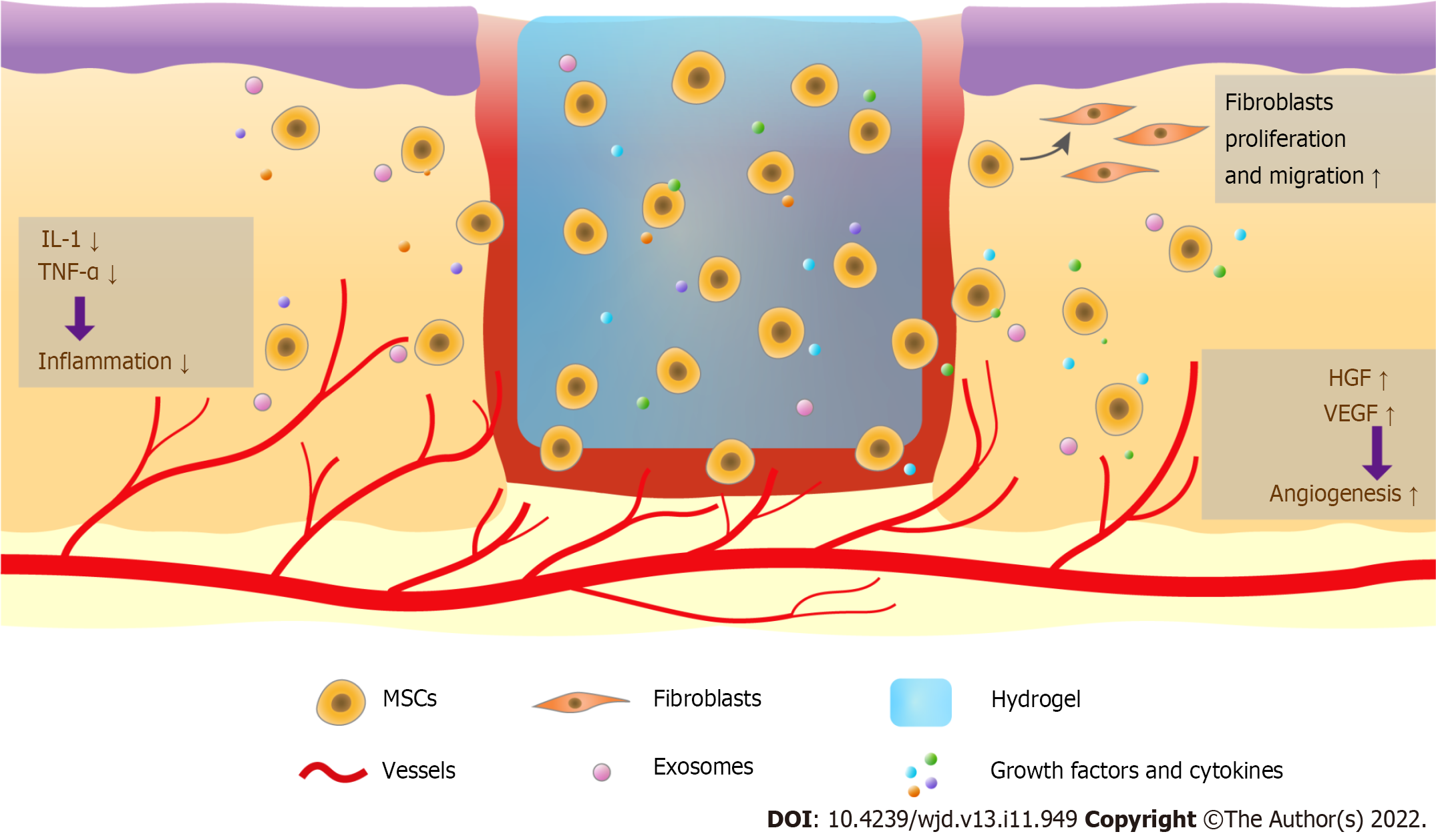
Figure 1 Therapy combining hydrogels and mesenchymal stem cells promotes diabetic wound healing.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in hydrogels are long-lasting in the wound and regulate wound healing. These cells release exosomes, growth factors, and cytokines, reduce the levels of interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor-α, and other pro-inflammatory cytokines to modulate the inflammatory response, enhance angiogenesis via increasing vascular endothelial growth factor and hepatocyte growth factor, and promote fibroblast and keratinocyte migration. MSCs can also be transdifferentiated into other cell types to increase wound closure. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; IL-1: Interleukin-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor.
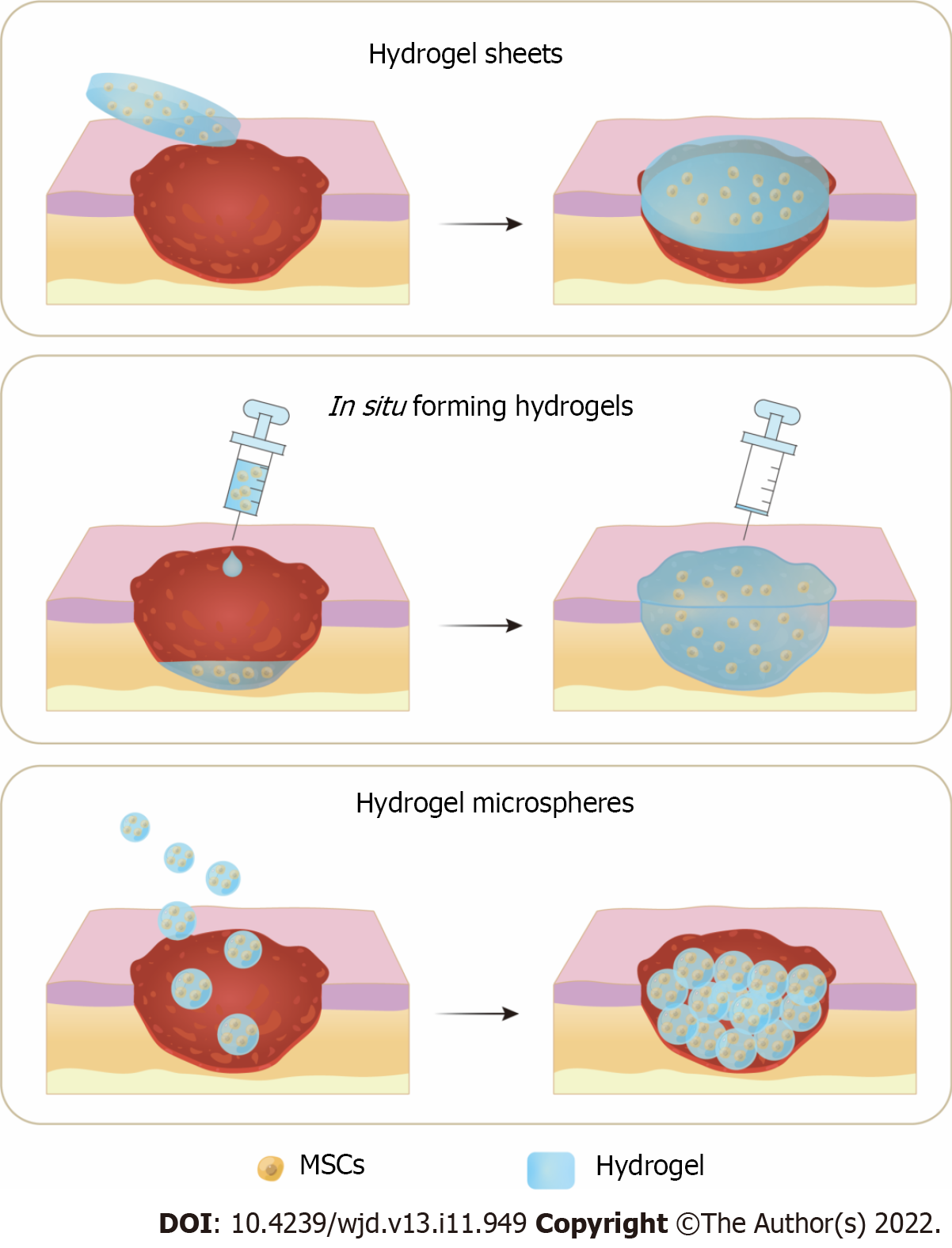
Figure 2 Three application methods of hydrogels and mesenchymal stem cells combination therapy for diabetic wound healing.
A: Hydrogel sheets preformed before application; B: In situ forming hydrogels injected at the wound for sol-gel transition; C: Hydrogel microspheres applied onto the diabetic wound. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Huang JN, Cao H, Liang KY, Cui LP, Li Y. Combination therapy of hydrogel and stem cells for diabetic wound healing. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(11): 949-961
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i11/949.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.949