Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Diabetes. Oct 15, 2020; 11(10): 435-446
Published online Oct 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i10.435
Published online Oct 15, 2020. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i10.435
Figure 1 Flowchart of cohort establishment.
PDAP: Peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis; DM: Diabetes mellitus.
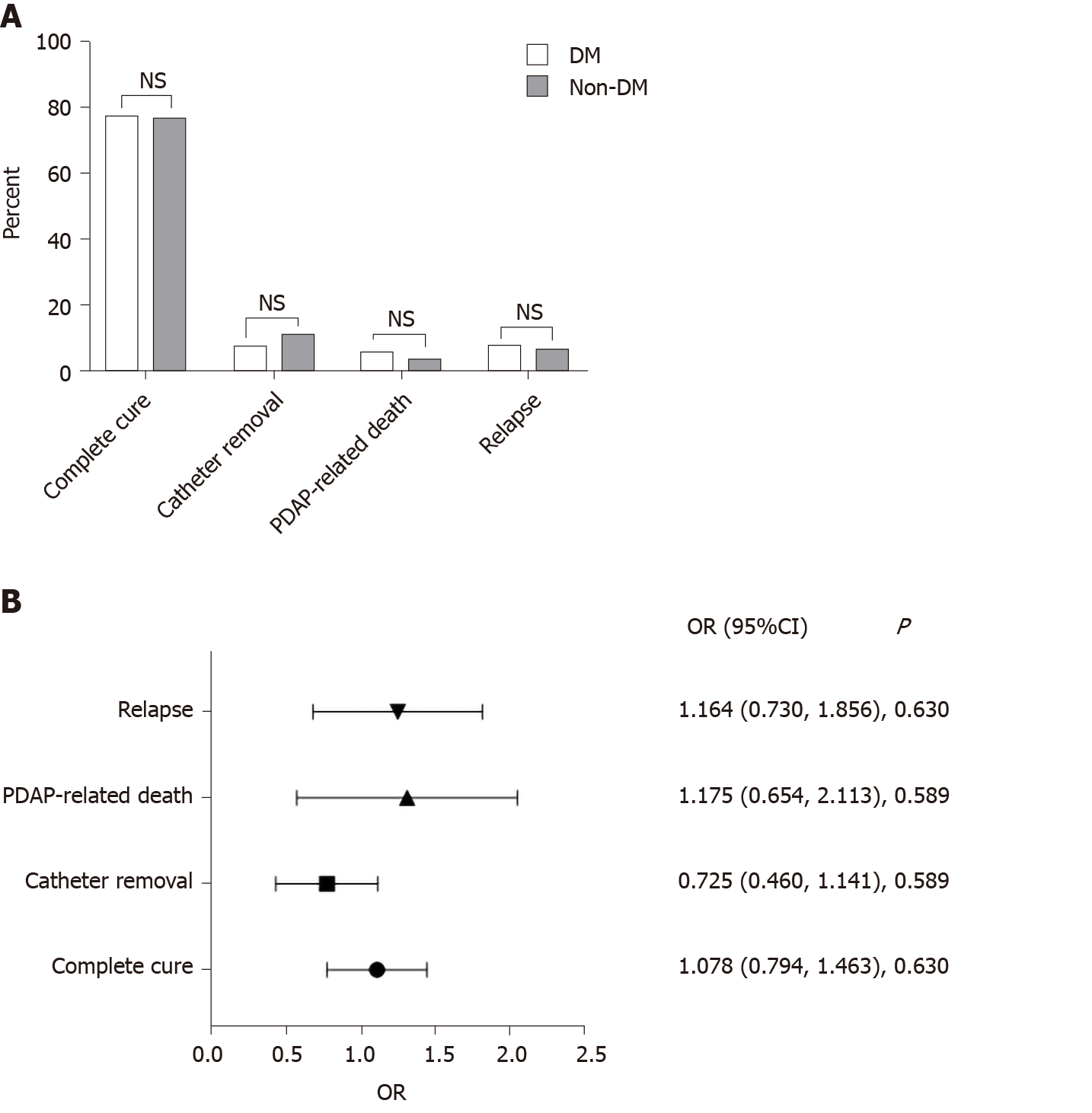
Figure 2 Association between diabetes mellitus and therapeutic outcomes of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis.
A: Therapeutic outcomes of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis (PDAP), including complete cure, catheter removal, PDAP-related death, and relapse of PDAP, between the two groups; B: Multivariable logistic regression analysis of relationship between diabetes mellitus and therapeutic outcomes of PDAP. Covariates with P < 0.05 in the univariate model and conventional confounders related to therapeutic outcomes (history of diabetes mellitus, age, gender, number of peritonitis episodes, history of cardiovascular diseases, basic hemoglobin, albumin, and estimated glomerular filtration rate) were included in the multivariate regression model. NS: Not significant; PDAP: Peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis; DM: Diabetes mellitus; OR: Odds ratio.
Figure 3 Association between diabetes mellitus and long-term prognostic outcomes of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis.
A: Long-term prognostic outcomes of PDAP, including all-cause death, technique failure, and on dialysis between the two groups; B and C: Kaplan-Meier analysis of cumulative patient survival and technique survival according to diabetes mellitus (DM); D: Cox regression analysis of relationship between DM and long-term prognostic outcomes. Covariates with P < 0.05 in the univariate model and conventional confounders related to long-term prognostic outcomes (history of DM, age, gender, times of peritonitis episodes, history of cardiovascular diseases, basic hemoglobin, albumin, and estimated glomerular filtration rate) were included in the multivariate regression model. aP < 0.05, compared between DM group and non-DM group. DM: Diabetes mellitus; HR: Hazard ratio.
- Citation: Meng LF, Yang LM, Zhu XY, Zhang XX, Li XY, Zhao J, Liu SC, Zhuang XH, Luo P, Cui WP. Comparison of clinical features and outcomes in peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis patients with and without diabetes: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. World J Diabetes 2020; 11(10): 435-446
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v11/i10/435.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v11.i10.435