Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 16, 2018; 10(9): 175-183
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175
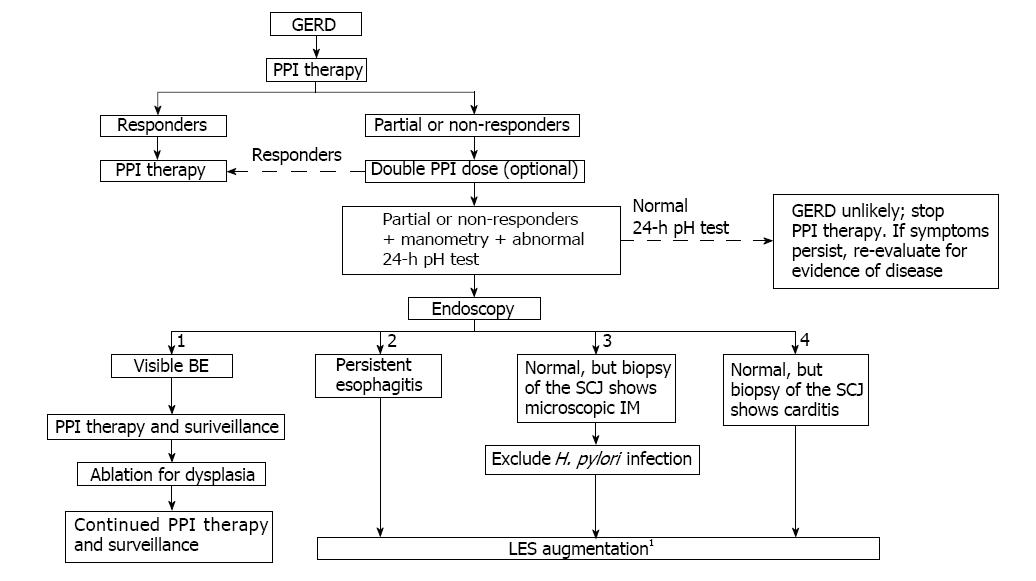
Figure 4 Proposed algorithm for the treatment of patients with progressive gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Patients who do not respond to PPI therapy and who have an abnormal 24-h esophageal pH should undergo endoscopy. Patients can be stratified into four groups following endoscopy: (1) patients with visible BE; (2) patients with persistent esophagitis; (3) patients with a normal endoscopy who have microscopic IM of the SCJ; and (4) patients with a normal endoscopy who have carditis at the SCJ. Patients in groups (2), (3) and (4) should undergo manometric assessment of LES function; those with a defective LES may be candidates for LES augmentation. 1If more than 2 permanently defective LES components consider Nissen fundoplication. BE: Barrett’s esophagus; GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; LES: Lower esophageal sphincter; IM: Intestinal metaplasia; PPI: Proton pump inhibitor; SCJ: Squamocolumnar junction.
- Citation: Labenz J, Chandrasoma PT, Knapp LJ, DeMeester TR. Proposed approach to the challenging management of progressive gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2018; 10(9): 175-183
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v10/i9/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175