Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2011; 17(23): 2812-2820
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2812
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2812
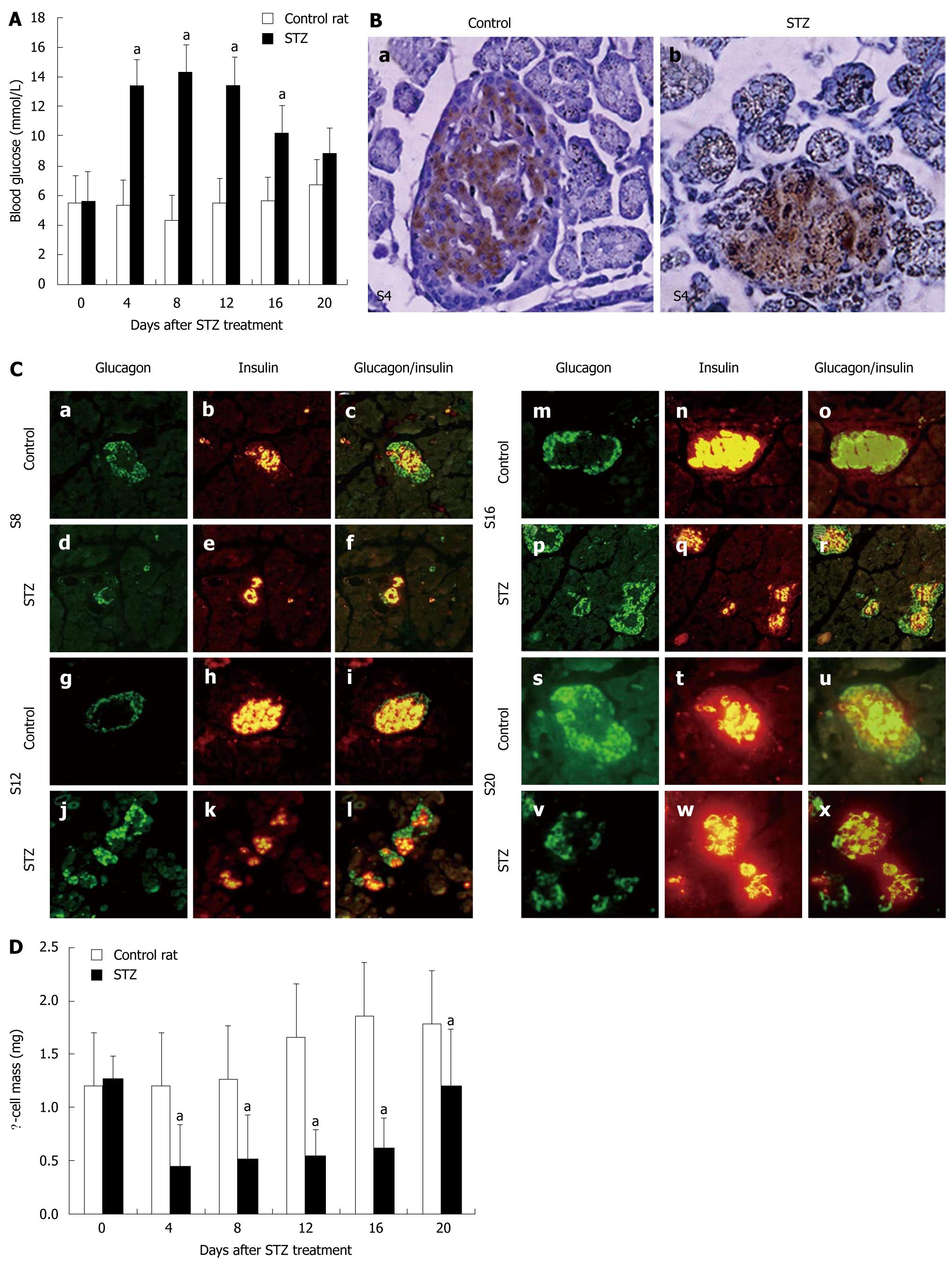
Figure 1 Body and pancreatic weight, blood glucose, islets and β-cell mass in streptozotocin-treated neonatal rat pancreas.
A: Concentrations of fasting blood glucose in control rats or rats treated with streptozotocin (STZ) between day 0 and day 20 after STZ treatment. Data were obtained from 12-18 animals at each time point. aP < 0.005 vs control; B: Immunohistochemical location of insulin in sections of rat pancreas in the control (a) and 4 d after STZ treatment; (b). Original magnification, × 400; C: Structure of islets in STZ-treated rats (d-f, j-l, p-r and v-x) and control rats (a-c, g-i, m-o and s-u) on d 8 (a-f), 12 (g-l), 16 (m-r) and 20 (s-x) after STZ treatment. Pancreatic sections were immunostained with anti-glucagon antibody (green) and anti-insulin antibody (red). Original magnification, × 400. Mean ± SD; D: β-cell mass in control rats or rats treated with STZ between day 0 and day 20 after STZ treatment. Data were obtained from three rats per time point. aP < 0.05 vs control rats.
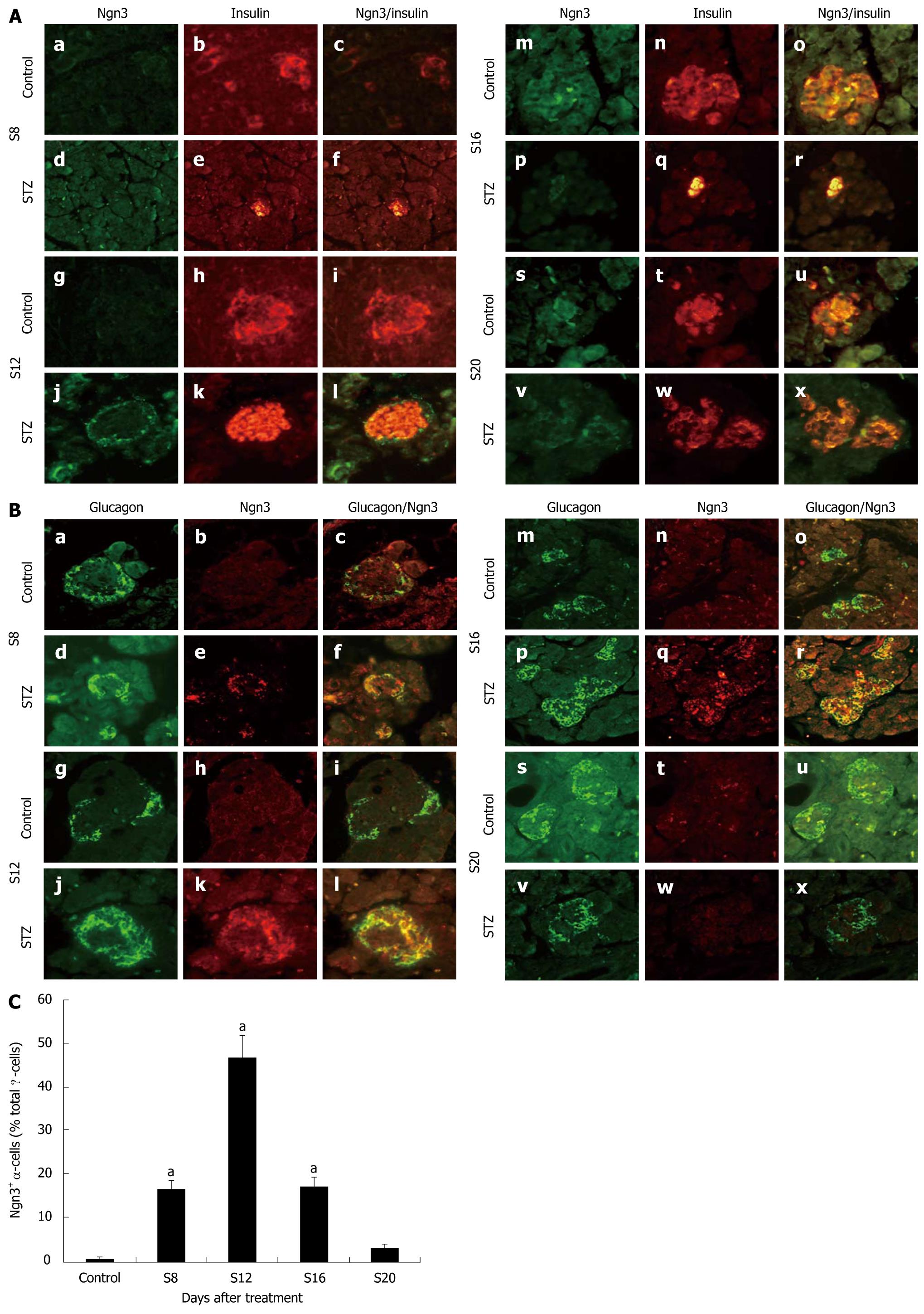
Figure 2 Expression and location of Ngn3.
A: Immunofluorescent colocalization of Ngn3 and insulin in streptozotocin (STZ)-treated rats (d-f, j-l, p-r and v-x) and control rats (a-c, g-i, m-o and s-u) on d 8 (a-f), 12 (g-l), 16 (m-r) and 20 (s-x) after STZ treatment. Pancreatic sections were immunostained with anti-Ngn3 antibody (green) and anti-insulin antibody (red). Original magnification, × 400; B: Immunofluorescent colocalization of Ngn3 and glucagon in STZ-treated rats (d-f, j-l, p-r and v-x) and control rats (a-c, g-i, m-o and s-u) on d 8 (a-f), 12 (g-l), 16 (m-r) and 20 (s-x) after STZ treatment. Pancreatic sections were immunostained with anti-glucagon antibody (green) and anti-Ngn3 antibody (red). Original magnification, × 400; C: Proportion of Ngn3+ / glucagon+ cells in total α-cells after treatment (Y). aP < 0.05 vs control rats.
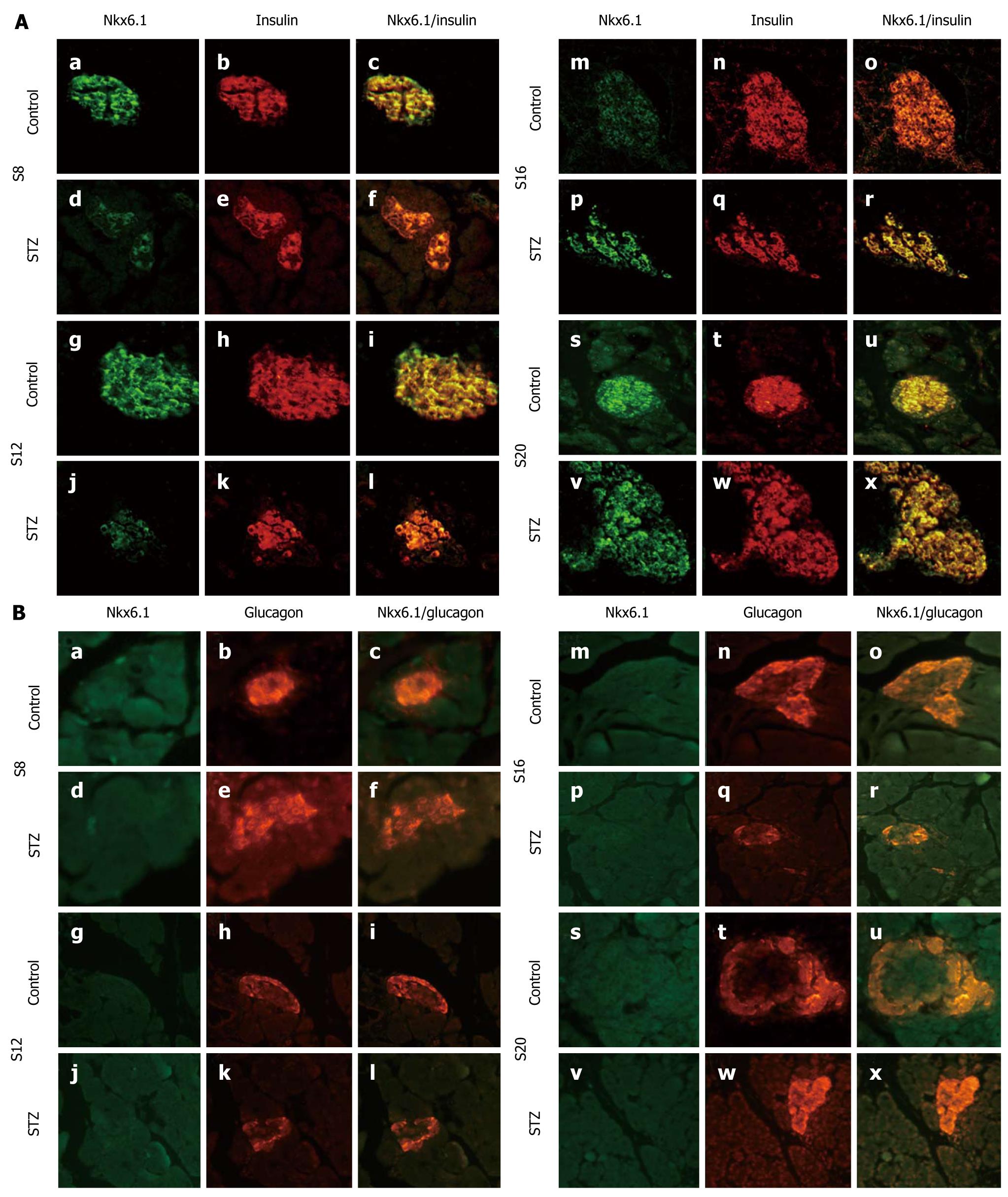
Figure 3 Expression and location of Nkx6.
1. A: Immunofluorescent colocalization of Nkx6.1 and insulin in streptozotocin (STZ)- treated rats (d-f, j-l, p-r and v-x) and control rats (a-c, g-i, m-o and s-u) on d 8 (a-f), 12 (g-l), 16 (m-r) and 20 (s-x) after STZ treatment. Pancreatic sections were immunostained with anti-Nkx6.1 antibody (green) and anti-insulin antibody (red); B: Immunofluorescent colocalization of Nkx6.1 and glucagon in STZ-treated rats (d-f, j-l, p-r and v-x) and control rats (a-c, g-i, m-o and s-u) on d 8 (a-f), 12 (g-l), 16 (m-r) and 20 (s-x) after STZ treatment. Pancreatic sections were immunostained with anti-Nkx6.1 antibody (green) and anti-glucagon antibody (red). Original magnification, × 400.
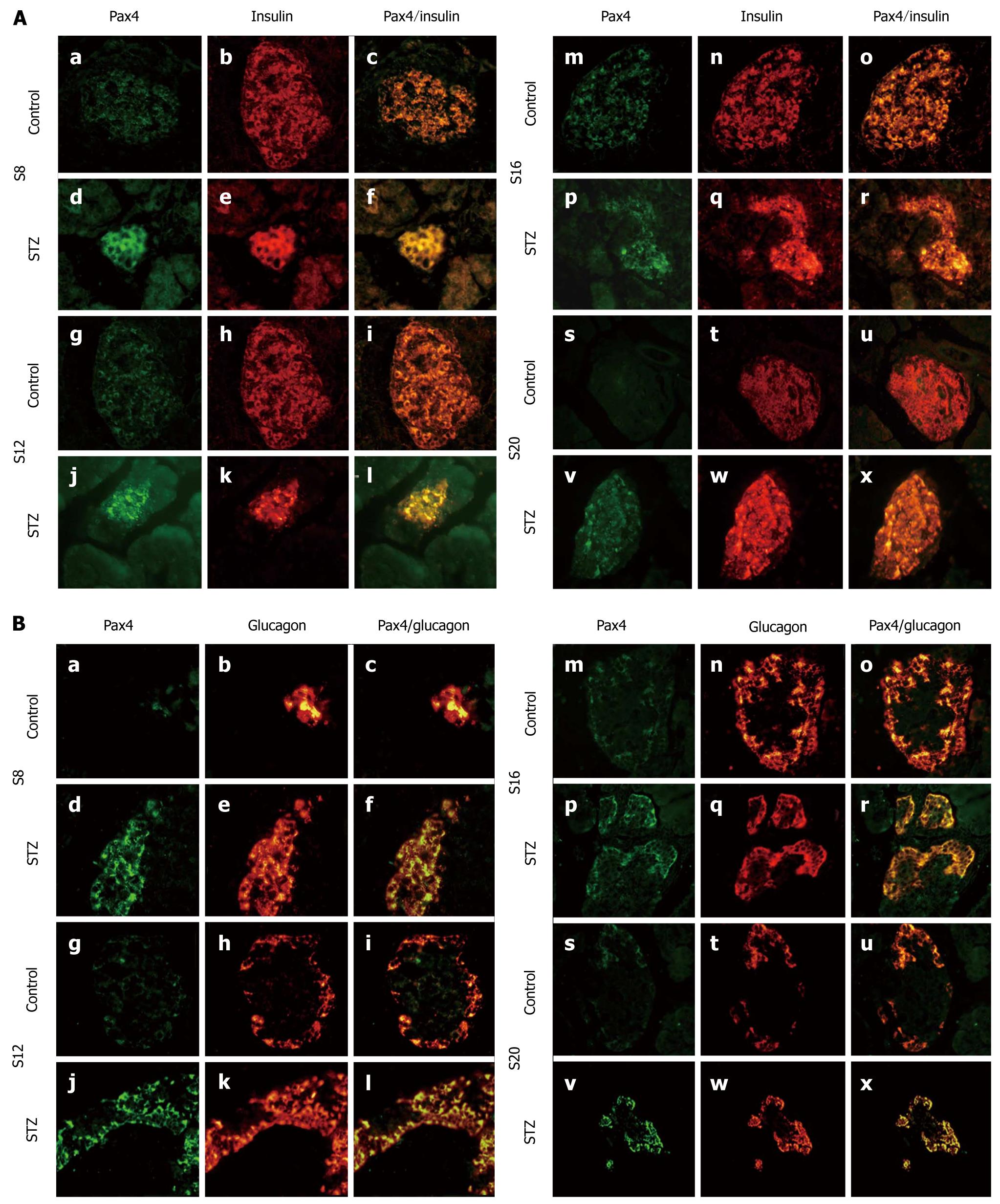
Figure 4 Expression and location of Pax4.
A: Immunofluorescent colocalization of Pax4 and insulin in streptozotocin (STZ)-treated rats (d-f, j-l, p-r and v-x) and control rats (a-c, g-i, m-o and s-u) on d 8 (a-f), 12 (g-l), 16 (m-r) and 20 (s-x) after STZ treatment. Pancreatic sections were immunostained with anti-Pax4 antibody (green) and anti-insulin antibody (red); B: Immunofluorescent colocalization of Pax4 and glucagon in STZ-treated rats (d-f, j-l, p-r and v-x) and control rats (a-c, g-i, m-o and s-u) on d 8 (a-f), 12 (g-l), 16 (m-r) and 20 (s-x) after STZ treatment. Pancreatic sections were immunostained with anti-Pax4 antibody (green) and anti-glucagon antibody (red). Original magnification, × 400.
- Citation: Liang XD, Guo YY, Sun M, Ding Y, Wang N, Yuan L, De W. Streptozotocin-induced expression of Ngn3 and Pax4 in neonatal rat pancreatic α-cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(23): 2812-2820
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i23/2812.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2812