Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2010; 16(15): 1845-1853
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1845
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1845
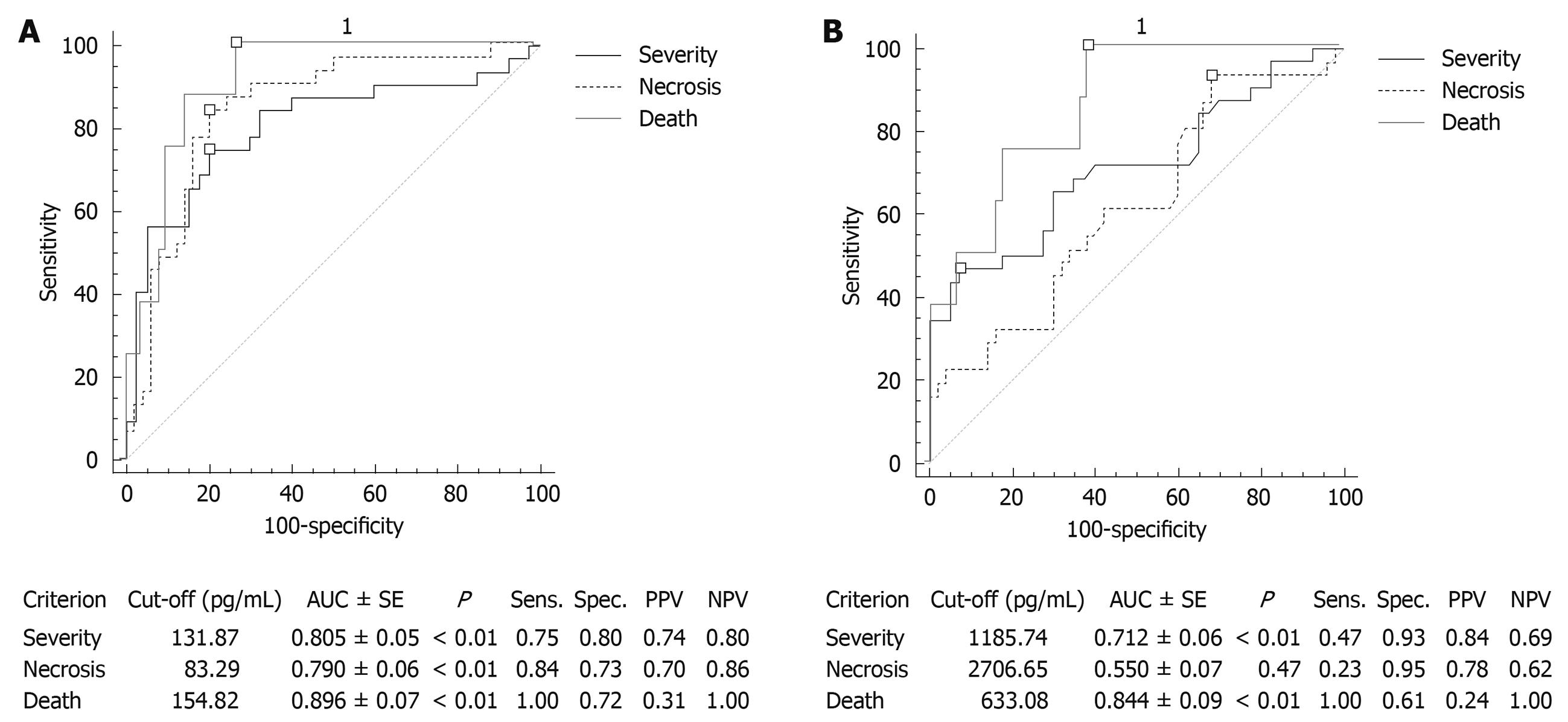
Figure 4 Prognostic utility of IL-6 and MIF in diagnosis of severe, necrotizing and fatal AP.
A: Performance of serum IL-6 in diagnosis of severe, necrotizing and fatal AP. The diagnostic performance of a test for discriminating severe, necrotizing and fatal cases of AP was evaluated using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Study revealed that serum IL-6 concentration is a good predictor of the severe disease and systemic complications (SIRS, MOF); this marker could also be utilized for the stratification of patients with necrotizing AP and those with possible fatal outcome; B: Performance of serum MIF in diagnosis of severe, necrotizing and fatal AP. The diagnostic performance of a test for discriminating severe, necrotizing and fatal cases of AP was evaluated using ROC curve analysis. Study revealed that serum MIF concentration is a good predictor of the severe disease and systemic complications (SIRS, MOF); this marker could be used for early identification of patients with possible fatal outcome. Comparison of ROC curves for IL-6 and MIF showed no statistically significant differences in this respect (P = 0.18 for severity; P = 0.58 for mortality). However, serum MIF concentration has very poor prognostic value in predicting the development of pancreatic necrosis and is inferior to IL-6 serum concentration in this respect (P < 0.01). AUC: Area under curve; Sens.: Sensitivity; Spec.: Specificity; PPV: Positive predictive value; NPV: Negative predictive value.
- Citation: Dambrauskas Z, Giese N, Gulbinas A, Giese T, Berberat PO, Pundzius J, Barauskas G, Friess H. Different profiles of cytokine expression during mild and severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(15): 1845-1853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i15/1845.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1845